Bottom line: Your odds of a successful recovery job are directly related to how long ago the files were deleted and how much you have used your computer since then. That's because, in the Windows file system, space occupied by a "deleted" file is marked as free space but the data once associated with it might still be intact. Once the space has been reused for a new file, however, it's gone.
Microsoft recently published an app on the Microsoft Store designed to help in the recovery of deleted files.
The app, appropriately named Windows File Recovery, is a command line utility that can attempt to recover deleted files from internal and external drives as well as USB devices and even SD cards. Supported file types include JPEG, PDF, PNG, MPEG, Office files, MP3 & MP4, ZIP files and more across NTFS, FAT, exFAT and ReFS file systems.
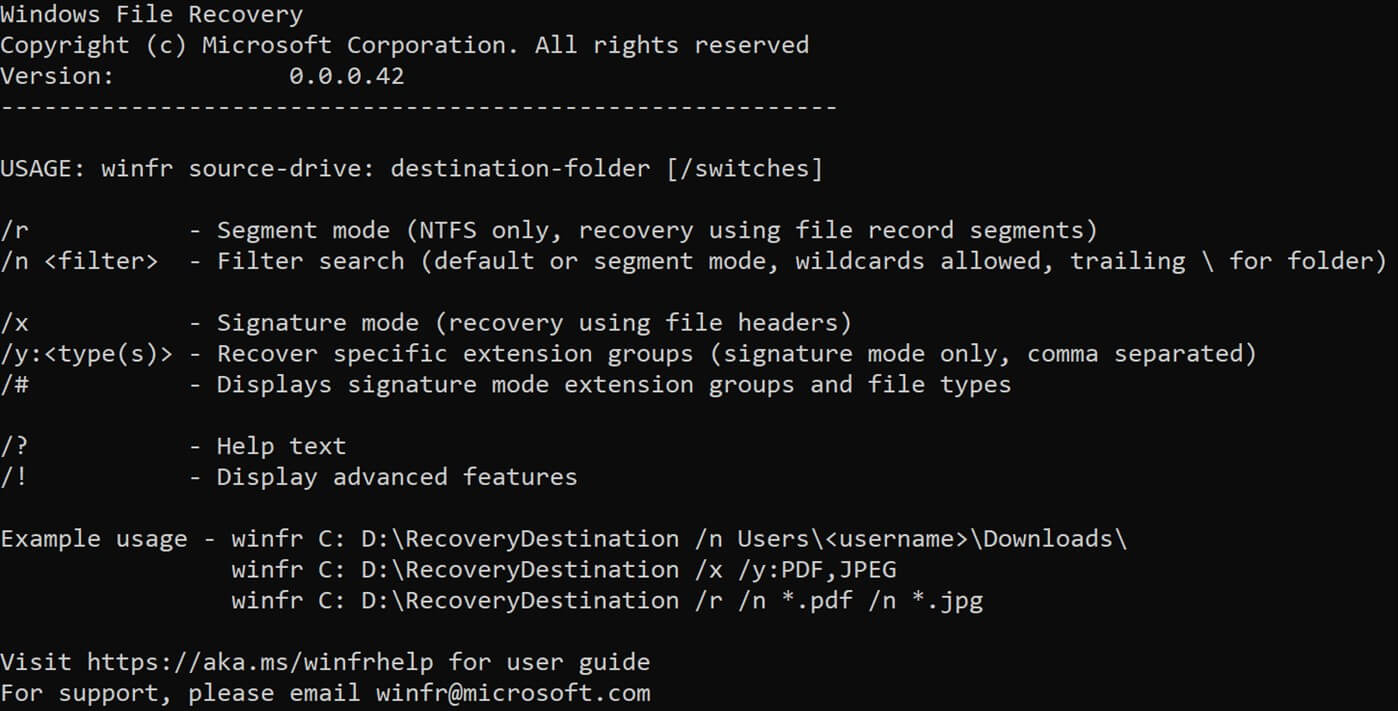
The tool offers three modes of operation: Default, Segment and Signature.
Default mode is recommended for NTFS files that were recently deleted. If you are dealing with content that was deleted a while ago or after formatting a disk, try Segment first, then Signature. Microsoft said Signature is also ideal when working with FAT, exFAT and ReFS file systems.
Notably, Microsoft said the tool can't be used for recovery of data on cloud storage or network file shares.
Microsoft's Windows File Recovery tool is available as a free download here.
Masthead credit: mike mols
